Section 01: Aggregate Demand
Long run: the money supply does not affect real variables (such as real GDP, real interest rate). Therefore classical theory allows us to study how real variables are determined without reference to the money supply. Then the equilibrium in the money market, equation (7), determines the price level and, as a result, all other nominal variables. The aggregate supply is the relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and the price level when all other influences on production plans (the money wage rate, the prices of other resources, and potential GDP) remain constant. The AS curve, as shown in Figure 6.1, is upward-sloping. Sep 29, 2017 How the GDP Affects Supply & Demand. The gross domestic product, or GDP, is a national indicator that represents the total demand for a nation’s goods and services over a given period. The response to changes in the GDP has an indirect influence on the local supply and demand for goods and services in a nation.
As discussed in the previous lesson, the aggregate expenditures model is a useful tool in determining the equilibrium level of output in the economy. It does have a significant flaw, however: the aggregate expenditures model does not take into account the impact of the price level on aggregate output. The Aggregate Demand Curve (AD) represents, in that sense, an even more appropriate model of aggregate output, because it shows the various amounts of goods and services which domestic consumers (C), businesses (I), the government (G), and foreign buyers (NX) collectively will desire at each possible price level. Let’s begin by showing the relationship between the aggregate expenditures model and the AD curve.
In the graph below, we show the standard aggregate expenditures curve at three different price levels. When prices are high (P1), Consumption is low; as prices fall to P2 and P3, Consumption rises. As the Consumption function shifts upward due to the falling prices, the equilibrium level of GDP goes up from GDP1 to GDP3. This is depicted in the AD framework as a downward sloping AD curve.
Why does it make sense for the AD curve to slope downward and to the right? We will suggest three different rationales for the downward sloped curve: the real balances effect, the interest rate effect, and the foreign purchases effect.
The Real Balances Effect
“Real balances” refers to the purchase power of a given amount of money in circulation. We make the assumption that at any given point in time, there is a fixed amount of money in circulation. At higher price levels, the money in circulation can purchase fewer items. Think of the simple of example of having $1,000 in circulation and the average price of the goods and services in the economy being $10. A total of 100 items could be purchased under these conditions. If the average price level were to rise to $20 per item, then the $1,000 in circulation would only allow us to purchase 50 items. At higher prices, the money in circulation will spread over fewer goods. When prices fall, the purchasing power of the money in circulation goes up, and people can buy more goods and services. This relationship between prices and the amount of goods and services that can be purchased with a given money supply is called the real balances effect. It justifies our depiction of the AD curve as a downward sloping curve.
The Interest Rate Effect
The interest rate effect explains impact that the price level has on interest rates, and thus on certain components of AD. When the price level goes up, people need more money to transact their daily purchases. Therefore, higher prices lead to an increase in the demand for money. With a fixed amount of money in circulation, increasing the demand for money will cause the interest rate to go up. Think of how you would behave if you were running a bank and the demand for money increased. You would try to encourage additional people to deposit money into the bank, and at the same time discourage people from coming into the bank to demand money. The way to do both simultaneously would be to increase the interest rate. As interest rates go up, investment demand and certain interest-rate sensitive consumption purchases will fall. Thus, increases in the price lead to increases the interest rate, which reduces the demand for both Consumption and Investment, and thus real output. The interest rate effect is therefore an additional justification for the downward sloping AD curve.
The Foreign Purchases Effect
Domestic prices also have an impact on Net Exports (NX) through what is called the foreign purchases effect. When US prices rise relative to world prices, foreigners buy fewer US goods and Americans buy more foreign goods, so NX fall. Since NX are part of AD, this contributes to an inverse relationship between the price level and the demand for our real domestic output. The opposite is also true. The foreign purchases effect contributes to our argument for why the AD is downward sloping.
Anything that changes the price level triggers these three effects and is represented by movement along a given AD curve. There are other factors that influence aggregate demand besides the price level, and these factors are referred to as determinants of AD. When these other factors change, they cause a shift in the entire AD curve and are sometimes called aggregate demand shifters. These aggregate demand shifters include anything that will influence the levels of Consumption, Investment, Government Spending, or Net Exports OTHER THAN changes in the price level. Let’s consider each in turn.
Section 02: Aggregate Demand Shifters
The graph below illustrates what a change in a determinant of aggregate demand will do to the position of the aggregate demand curve. As we consider each of the determinants remember that those factors that cause an increase in AD will shift the curve outward and to the right and those factors that cause a decrease in AD will shift the curve inward and to the left.
Changes in Consumption unrelated to a change in the price
There are several factors that could increase or decrease consumption that are unrelated to changes in the price level. For instance, increases in consumer wealth would increase consumption at each price level and would be illustrated by a rightward shift in AD. Decreases in consumer wealth would have the opposite effect. Increases in consumer indebtedness would decrease consumption and shift the aggregate demand curve to the left, while decreases in indebtedness would have the opposite effect. Increases in taxes will decrease consumption (and shift the AD curve to the left) while decreases in taxes will increase consumption and shift the AD curve to the right. Consumer expectations about the future of the economy can have a strong impact on consumptions. Optimism about the economy will increase consumption and shift the AD curve to the right, while widespread pessimism dampens consumer spending and shifts the AD curve to the left. You can probably think of other factors that will shift the AD curve because they impact consumption independent of the price level.
Changes in Investment unrelated to a change in the price
There are several factors unrelated to changes in the price level that could increase or decrease Investment and thereby shift the AD curve. For instance, any change in the interest rate not brought about by a change in the price level would change the level of investment in the economy, and shift the AD curve. Increases in the interest rate will reduce investment demand; decreases in the interest rate will increase investment demand. Business taxes can be structured to either encourage investment (shifting the AD to the right) or discourage investment (shifting AD to the left). Technological improvements in an industry might make old equipment obsolete and stimulate investment, shifting AD to the right. Finally, like the impact of expectations on consumers, optimism (or pessimism) on the part of business owners can lead to increases (or decreases) in investment activity and shift the AD curve to the right (or left).
Changes in Government Spending unrelated to a change in the price
The political process will sometimes lead to increases or decreases in the level of government spending. Increases in government spending will shift the AD curve to the right; decreases in government spending will shift the AD curve to the left.
Changes in Net Exports unrelated to changes in the price
There are two important factors unrelated to the price level that could increase or decrease the level of Net Exports and thereby shift the AD Curve. The first has to do with changes in national income abroad. As income abroad grows relative to income in the United States, foreigners are able to buy US products more easily and Americans can afford fewer foreign goods. Net exports will go up, shifting the AD curve to the right. If incomes abroad fall relative to income in the US, the AD curve will shift left due to a decrease in net exports. The second factor has to do with exchange rates, or the relative value of our currency to the currency of a trading partner. As an example, let’s say that it takes 90 Japanese Yen to buy one US dollar. If the value of the yen relative to the dollar changes so that it takes 100 Yen to buy one US dollar, this will decrease the amount that Japanese citizens will buy in the US, and increase the amount that US citizens can buy in Japan. This change in the exchange rate will cause net exports to fall and the AD curve to shift to the left. If the Japanese Yen were to appreciate relative to the dollar, net exports would rise and the AD curve would shift to the right.
Return to the course in I-Learn and complete the activity that corresponds with this material.
Section 03: Aggregate Supply
Aggregate Supply (AS) is a curve showing the level of real domestic output available at each possible price level. Typically AS is depicted with an unusual looking graph like the one shown below. There is a specific reason for why the AS has this peculiar shape. The AS curve can be separated into three distinct ranges called the Keynesian Range, the Intermediate Range, and the Classical Range. The various ranges depict three different states in which the economy may find itself. The three states of the economy can all be thought of in relation to what is called the full-employment level of output, labeled Qf in the graph below. We will now discuss each of the three ranges of the AS.
In the Keynesian range of AS, we are at outputs which are substantially below Qf. This horizontal range implies an economy in severe recession or depression. Remember that Keynes wrote his General Theory during the heights of the Great Depression, so the range of AS that is associated with his name corresponds to such an economy. Assume that you were running a factory during a severe recession with high unemployment, and you decided that you would like to increase output. You realize that, to increase output, you are going to have to employ more inputs, primarily more labor—however, a similar argument could be made about high unemployment of any of the other factors of production. You go to the factory door, open it, and find thousands of unemployed workers standing in line, wanting to work at your factory. How much would you have to pay them to get them to go to work for you? Certainly, you would not have to pay them more than the going wage rate in the market, right? Essentially, you could hire as many unemployed resources as you would like without bidding up wages and prices, because of the substantial unemployment. The horizontal or Keynesian AS illustrates the idea of the economy being able to increase real output with no increase in the price level during periods of high unemployment. This range of the AS curve is also sometimes referred to as the Short Run AS curve.
In the Classical Range of AS, we are at or very near the full-employment level of output. This range is named after the Classical Economists who assumed that the economy, in the long run, would always achieve full employment. The Classical AS curve is sometimes called the Long Run AS curve. Assume again that you are running a factory, only this time, the economy is at full-employment. Let’s say again that you want to increase output, and that in order to do so you have to increase the number of workers at your factory. You go to the factory door and open it to find nobody waiting in line. There does not appear to be anyone looking for a job because everyone already has one! In order to hire additional workers, you go to other employers’ workers, and ask them to leave their job to work for you. How much are you going to have to pay these workers to get them to do that? Most likely you will have to pay them more than they are currently making. As you bid up wages in the labor market to attract additional workers, prices in the economy will also rise, because now it costs more to produce your product. That additional cost is passed to the consumer in the form of higher prices, to the extent possible. Attempts to increase output in the Classical Range leads to higher price levels in the economy but what about real GDP? Does it actually increase? Well, your output may go up, but the output of the factory where your new workers used to work will go down, so the overall output in the economy stays the same at Qf.
In the Intermediate Range, we are at output levels that are below full employment, but not so far below as to constitute a deep recession or depression. In this range, increasing output is possible, but only at the expense of rising prices. While that Keynesian Range is a rare short-run occurrence, and the Classical Range is the long-run steady state of the economy, the Intermediate Range is probably where we find ourselves most often in the economy.
Depending on the state of the economy, any attempt to change the output of the economy will move us along a given AS curve. There are factors that influence aggregate supply, illustratable by shifting the AS curve—these factors are referred to as determinants of AS. When these other factors change, they cause a shift in the entire AS curve and are sometimes called aggregate supply shifters. These aggregate supply shifters include Changes in Resource Prices, Changes in Resource Productivity, Business Taxes and Subsidies, and Government Regulations. Let’s consider each in turn.
Section 04: Determinants of Aggregate Supply
The graph below illustrates what a change in a determinant of aggregate supply will do to the position of the aggregate supply curve. As we consider each of the determinants remember that those factors that cause an increase in AS will shift the curve outward and to the right and those factors that cause a decrease in AS will shift the curve upward and to the left.
Changes in Input Prices
Anything that causes input prices to rise will decrease AS and shift the AS curve to the left. Anything that causes input prices to fall will increase AS and shift the AS curve to the right. For instance, if a particular input into the production process is readily available from domestic suppliers, it will generally be cheaper, holding all else constant (cet. par.). If for no other reason, transportation costs of delivering a domestic resource to a domestic producer will be less than delivering the identical resource from a foreign supplier. That does not even take into account the problems of getting a foreign resource such as duties and tariffs, political or social instability abroad, or other international disruptions. Another factor that can influence input prices would be the market power of the suppliers of the resource. The more competition in the supply of a resource, the cheaper that resource will be, cet. par. If the resource is supplied by a monopolist or a cartel (think OPEC oil), the price of that resource will be higher than if the resource is supplied by a more competitive industry (think corn-produced ethanol).
Changes in Productivity
Independent of its price, anything that makes resources more productive will increase AS and shift the AS curve to the right; anything that makes resources less productive will decrease AS and shift the AS curve to the left. If workers become more productive because of investments in physical or human capital, the economy will be able to produce more and the AS curve will shift to the right. If workers become less productive because of outmoded equipment, insufficient training, or excessive union interference in their workplace, the economy will be less productive, and the AS curve will shift to the left.

Business Taxes and Subsidies
In brief, business taxes increase the cost of production and shift the AS curve to the left; subsidies decrease the cost of production and shift the AS curve to the right.
Government Regulations
Government regulations also influence the costs of production. Increasing government regulations makes it more expensive to produce the nation’s output and shifts the AS curve to the left; reducing government regulations lessens the burden of business and shifts the AS curve to the right.
Return to the course in I-Learn and complete the activity that corresponds with this material.
Section 05: Equilibrium
What does the equilibrium between AD and AS determine? The Price Level in the economy and the Real Output (GDP) of the economy. Equilibrium is illustrated below as the intersection between AD and AS.
Section 06: Shifts in the AD Curve
Let’s review all of the possible impacts on the price level and the level of real GDP from a shift in the AD curve. An increase in the AD in the Keynesian Range of AS will increase Real Output, but leave the Price Level the same; a decrease in AD in the Keynesian Range of the AS will decrease Real Output but leave the Price Level the same.
An increase in AD in the Intermediate Range of AS will increase Real Output and increase the Price Level; a decrease in AD in the Intermediate Range of AS will decrease Real Output and decrease the Price Level. Notice that in the intermediate range, there is a tradeoff between two of the key economic variables that concern US citizens: Inflation and Unemployment. Typically, we would like both inflation and unemployment to be low. In the intermediate range, however, if we increase AD, inflation will go up as unemployment falls (notice that if real GDP is going up, unemployment is going down: in order to increase GDP, you have to hire more workers). On the other hand, if we decrease AD, inflation will fall but unemployment will rise. There is no way to simultaneously decrease inflation and decrease unemployment using demand side shifts.
An increase in AD in the Classical Range of AS will leave Real Output unchanged, but will increase the Price Level. A decrease in AD in the Classical Range of AD will leave Real Output unchanged, but will lower the Price Level.
The price increases that result from increases in AD are examples of Demand-Pull Inflation
Do you think that decreases in AD have exactly the opposite effects as the increases? Typically they do, but there is a possibility of inflexibility downward of prices due to the “ratchet effect.” In economics, the ratchet effect states that while prices are quick to increase, they are very slow to fall. Why do you think that prices would go up very easily but fall only slowly? Part of the answer has to do with the fact that it actually costs businesses money to change their prices (think of printing new catalogs, printing new menus, recoding prices in a computer and on scanners, or sending a worker out to change the prices on a marquee). It is worth it to the business to incur this expense when the price is going up, but when the price is going down they are hesitant to take on the expense of changing prices!
Section 07: Shifts in Aggregate Supply
A decrease in AS will increase the Price Level and decrease Real Output. An increase in AS will reduce the Price Level and increase Real Output. The inflation that is associated with a decrease in the AS is called Cost-Push Inflation. During the 1970s, a variety of factors shifted the AS curve to the left. The high inflation that was combined with a stagnant economy (low levels of output and high unemployment) gave rise to the term Stagflation.
When Ronald Reagan was elected President in 1980, the inflation rate was 13.5% and the unemployment rate was 7.5%. Reagan employed supply side policies that were designed to shift the AS curve to the right and reduce both inflation and unemployment simultaneously. Only by supply side policies can you decrease both inflation and unemployment at the same time. By the time that Reagan left office eight years later, the inflation rate in the economy was 4.1% and the unemployment rate of 5.3%.
Think About It: Understanding Supply Side Shifters
Looking back at the AS shifters, come up with what some effective supply side policies might be.
Section 08: The Recessionary and Inflationary Gaps Revisited
When the AD curve intersects the AS curve in the Keynesian Range or in the Intermediate Range such that output is below Qf, there exists what is called a recessionary gap. The gap represents the amount of government spending that would be necessary to shift the AD to the right enough to bring output to Qf. In the Keynesian Model, the magnitude of the shift in AD will depend on the size of the multiplier. For example, if the multiplier is 2.5, a 40 million dollar increase in government spending would shift the AD curve to the right by 100 million dollars. So if the AD needs to be shifted to the right by 100 million dollars to get to Qf and the multiplier is 2.5, there is a 40 million dollar recessionary gap. Conversely, if the AD needs to be shifted to the left to get to Qf, there is an inflationary gap and the same multiplier principles would apply.
The changes in government spending that would close an inflationary or recessionary gap are applications of fiscal policy, which is the topic of our next lesson.
The Impact of Monetary Policy on Aggregate Demand, Prices, and Real GDP
Changes in a country’s money supply shifts the country’s aggregate demand curve.
Learning Objectives
Recognize the impact of monetary policy on aggregate demand
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Aggregate demand (AD) is the sum of consumer spending, government spending, investment, and net exports.
- The AD curve assumes that money supply is fixed.
- The decrease in the money supply is mirrored by an equal decrease in the nominal output, otherwise known as Gross Domestic Product ( GDP ).
- The decrease in the money supply will lead to a decrease in consumer spending. This decrease will shift the AD curve to the left.
- The increase in the money supply is mirrored by an equal increase in nominal output, or Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- The increase in the money supply will lead to an increase in consumer spending. This increase will shift the AD curve to the right.
- Increased money supply causes reduction in interest rates and further spending and therefore an increase in AD.
Key Terms
- aggregate demand: The the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level.
Aggregate demand (AD) is the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level. It is the combination of consumer spending, investments, government spending, and net exports within a given economic system (often written out as AD = C + I + G + nX). As a result of this, increases in overall capital within an economy impacts the aggregate spending and/or investment. This creates a relationship between monetary policy and aggregate demand.
This brings us to the aggregate demand curve. It specifies the amounts of goods and services that will be purchased at all possible price levels. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a country. It is also referred to as the effective demand.
The aggregate demand curve illustrates the relationship between two factors – the quantity of output that is demanded and the aggregated price level. Another way of defining aggregate demand is as the sum of consumer spending, government spending, investment, and net exports. The aggregate demand curve assumes that money supply is fixed. Altering the money supply impacts where the aggregate demand curve is plotted.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Contractionary monetary policy decreases the money supply in an economy. The decrease in the money supply is mirrored by an equal decrease in the nominal output, otherwise known as Gross Domestic Product (GDP). In addition, the decrease in the money supply will lead to a decrease in consumer spending. This decrease will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left. This reduction in money supply reduces price levels and real output, as there is less capital available in the economic system.
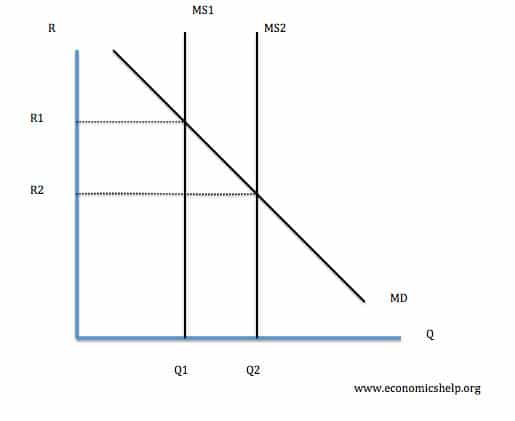
Aggregate Demand Graph: This graph shows the effect of expansionary monetary policy, which shifts aggregate demand (AD) to the right.
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Expansionary monetary policy increases the money supply in an economy. The increase in the money supply is mirrored by an equal increase in nominal output, or Gross Domestic Product (GDP). In addition, the increase in the money supply will lead to an increase in consumer spending. This increase will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.
In addition, the increase in money supply would lead to movement up along the aggregate supply curve. This would lead to a higher prices and more potential real output.
The Effect of Expansionary Monetary Policy
An expansionary monetary policy is used to increase economic growth, and generally decreases unemployment and increases inflation.
Learning Objectives
Analyze the effects of expansionary monetary policy
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- The primary means a central bank uses to implement an expansionary monetary policy is through purchasing government bonds on the open market.
- Another way to enact an expansionary monetary policy is to increase the amount of discount window lending.
- A third method of enacting a expansionary monetary policy is by decreasing the reserve requirement.
Key Terms
- expansionary monetary policy: Traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding.
- unemployment: The state of being jobless and looking for work.
Monetary policy is referred to as either being expansionary or contractionary. Expansionary policy seeks to accelerate economic growth, while contractionary policy seeks to restrict it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. This is done by increasing the money supply available in the economy.
Expansionary policy attempts to promote aggregate demand growth. As you may remember, aggregate demand is the sum of private consumption, investment, government spending and imports. Monetary policy focuses on the first two elements. By increasing the amount of money in the economy, the central bank encourages private consumption. Increasing the money supply also decreases the interest rate, which encourages lending and investment. The increase in consumption and investment leads to a higher aggregate demand.
It is important for policymakers to make credible announcements. If private agents (consumers and firms) believe that policymakers are committed to growing the economy, the agents will anticipate future prices to be higher than they would be otherwise. The private agents will then adjust their long-term plans accordingly, such as by taking out loans to invest in their business. But if the agents believe that the central bank’s actions are short-term, they will not alter their actions and the effect of the expansionary policy will be minimized.
The Basic Mechanics of Expansionary Monetary Policy
A central bank can enact an expansionary monetary policy several ways. The primary means a central bank uses to implement an expansionary monetary policy is through open market operations. Commonly, the central bank will purchase government bonds, which puts downward pressure on interest rates. The purchases not only increase the money supply, but also, through their effect on interest rates, promote investment.
Because the banks and institutions that sold the central bank the debt have more cash, it is easier for them to make loans to its customers. As a result, the interest rate for loans decrease. Businesses then, presumably, use the money it borrowed to expand its operations. This leads to an increase in jobs to build the new facilities and to staff the new positions.
The increase in the money supply is inflationary, though it is important to note that, in practice, different monetary policy tools have different effects on the level of inflation.
Other Methods of Enacting Expansionary Monetary Policy
Another way to enact an expansionary monetary policy is to increase the amount of discount window lending. The discount window allows eligible institutions to borrow money from the central bank, usually on a short-term basis, to meet temporary shortages of liquidity caused by internal or external disruptions. Decreasing the rate charged at the discount window, the discount rate, will not only encourage more discount window lending, but will put downward pressure on other interest rates. Low interest rates encourage investment.
Bank of England Interest Rates: The Bank of England (the central bank in England) undertook expansionary monetary policy and lowered interest rates, promoting investment.
Another method of enacting a expansionary monetary policy is by decreasing the reserve requirement. All banks are required to have a certain amount of cash on hand to cover withdrawals and other liquidity demands. By decreasing the reserve requirement, more money is made available to the economy at large.
The Effect of Restrictive Monetary Policy
A restrictive monetary policy will generally increase unemployment and decrease inflation.
Learning Objectives
Analyze the effects of restrictive monetary policy
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Another way to enact a restrictive monetary policy is to decrease the amount of discount window lending.
- A final method of enacting a restrictive monetary policy is by increasing the reserve requirement.
- The primary means a central bank uses to implement an expansionary monetary policy is through open market operations. The central bank can issue or resell its debt in exchange for cash. It can also sell off some of its reserves in gold or foreign currencies.
Key Terms
- contractionary monetary policy: Central bank actions designed to slow economic growth.
Monetary policy is can be classified as expansionary or restrictive (also called contractionary). Restrictive monetary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it, while and expansionary policy increases the money supply. It is intended to slow economic growth and/or inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values
Business cycle: Restrictive monetary policy is used during expansion and boom periods in the business cycle to prevent the overheating of the economy.
Contractionary policy attempts to slow aggregate demand growth. As you may remember, aggregate demand is the sum of private consumption, investment, government spending and imports. Monetary policy focuses on the first two elements. By decreasing the amount of money in the economy, the central bank discourages private consumption. Increasing the money supply also increase the interest rate, which discourages lending and investment. The higher interest rate also promotes saving, which further discourages private consumption. The decrease in consumption and investment leads to a decrease in growth in aggregate demand.
It is important for policymakers to make credible announcements. If private agents (consumers and firms) believe that policymakers are committed to limiting inflation through restrictive monetary policy, the agents will anticipate future prices to be lower than they would be otherwise. The private agents will then adjust their long-term strategies accordingly, such as by putting plans to expand their operations on hold. But if the agents believe that the central bank’s actions will soon be reversed, they may not alter their actions and the effect of the contractionary policy will be minimized.
The Basic Mechanics of Expansionary Monetary Policy
A central bank can enact a contractionary monetary policy several ways. The primary means a central bank uses to implement an expansionary monetary policy is through open market operations. The central bank can issue debt in exchange for cash. This results in less cash being in the economy.
Because the banks and institutions that purchased the debt from the central bank have less cash, it is harder for them to make loans to its customers. As a result, the interest rate for loans increase. Businesses then, presumably, have less money to use to expand its operations or even maintain its current levels. This could lead to an increase in unemployment.
The higher interest rates also can slow inflation. Consumption and investment are discouraged, and market actors will choose to save instead of circulating their money in the economy. Effectively, the money supply is smaller, and there is reduced upward pressure on prices since demand for consumption goods and services has dropped.
Other Methods of Enacting Restrictive Monetary Policy
Another way to enact a contractionary monetary policy is to decrease the amount of discount window lending. The discount window allows eligible institutions to borrow money from the central bank, usually on a short-term basis, to meet temporary shortages of liquidity caused by internal or external disruptions
A final method of enacting a contractionary monetary policy is by increasing the reserve requirement. All banks are required to have a certain amount of cash on hand to cover withdrawals and other liquidity demands. By increasing the reserve requirement, less money is made available to the economy at large.
Limitations of Monetary Policy
Limitations of monetary policy include liquidity traps, deflation, and being canceled out by other factors.
Learning Objectives
Describe obstacles to the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy objectives
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- A liquidity trap is a situation where injections of cash into the private banking system by a central bank fail to lower interest rates and therefore fail to stimulate economic growth.
- Deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt and may aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral.
- Fiscal policy can also directly influence employment and economic growth. If these two policies do not work in concert, they can cancel each other out.
Key Terms
- deflation: A decrease in the general price level, that is, in the nominal cost of goods and services.
Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money with the purpose of promoting stable employment, prices, and economic growth. Monetary policy can influence an economy but it cannot control it directly. There are limits as to what monetary policy can accomplish. Below are some of the factors that can make monetary policy less effective.
Multiple Factors Influencing Economy
While monetary policy can influence the elements listed above, it is not the only thing that does. Fiscal policy can also directly influence employment and economic growth. If these two policies do not work in concert, they can cancel each other out. This is an especially significant problem when fiscal policy and monetary policy are controlled by two different parties. One party might believe that the economy is teetering on recession and may pursue an expansionary policy. The other group may believe the economy is booming and pursue a contractionary policy. The result is that the two would cancel each other, so that neither would influence the direction of the economy.
Liquidity Trap
A liquidity trap is a situation where injections of cash into the private banking system by a central bank fail to lower interest rates and therefore fail to stimulate economic growth. Usually central banks try to lower interest rates by buying bonds with newly created cash. In a liquidity trap, bonds pay little to no interest, which makes them nearly equivalent to cash. Under the narrow version of Keynesian theory in which this arises, it is specified that monetary policy affects the economy only through its effect on interest rates. Thus, if an economy enters a liquidity trap, further increases in the money stock will fail to further lower interest rates and, therefore, fail to stimulate.
Liquidity Trap: Sometimes, when the money supply is increased, as shown by the Liquidity Preference-Money Supply (LM) curve shift, it has no impact on output (GDP or Y) or on interest rates. This is a liquidity trap.
A liquidity trap is caused when people hoard cash because they expect an adverse event such as deflation, insufficient aggregate demand, or war. Signature characteristics of a liquidity trap are short-term interest rates that are near zero and fluctuations in the monetary base that fail to translate into fluctuations in general price levels.
Deflation
Deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0%. This should not be confused with disinflation, a slowdown in the inflation rate. Inflation reduces the real value of money over time; conversely, deflation increases the real value of money. This allows one to buy more goods with the same amount of money over time.
From a monetary policy perspective, deflation occurs when there is a reduction in the velocity of money and/or the amount of money supply per person. The velocity of money is the frequency at which one unit of currency is used to purchase domestically-produced goods and services within a given time period. In other words, it is the number of times one dollar is spent to buy goods and services per unit of time. If the velocity of money is increasing, then more transactions are occurring between individuals in an economy.
Deflation is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt and may aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral. If monetary policy is too contractionary for too long, deflation could set in.
Using Monetary Policy to Target Inflation
Inflation targeting occurs when a central bank attempts to steer inflation towards a set number using monetary tools.
Learning Objectives
Assess the use of inflation targets and goals in monetary policy
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Because interest rates and the inflation rate tend to be inversely related, the likely moves of the central bank to raise or lower interest rates become more transparent under the policy of inflation targeting.
- If inflation appears to be above the target, the bank is likely to raise interest rates; if inflation appears to be below the target, the bank is likely to lower interest rates.
- Increases in inflation, measured by the consumer price index (CPI), are not necessarily coupled to any factor internal to country’s economy and strictly or blindly adjusting interest rates will potentially be ineffectual and restrict economic growth when it was not necessary to do so.
Key Terms

- consumer price index: A statistical estimate of the level of prices of goods and services bought for consumption purposes by households.
Inflation targeting is an economic policy in which a central bank estimates and makes public a projected, or “target”, inflation rate and then attempts to steer actual inflation towards the target through the use of interest rate changes and other monetary tools.
Fed Reserve Seal: The United States Federal Reserve uses a form of inflation targeting when coordinating its monetary policy.
Because interest rates and the inflation rate tend to be inversely related, the likely moves of the central bank to raise or lower interest rates become more transparent under the policy of inflation targeting. Examples include:
How Does Supply Of Money Affect Real Gdp
- if inflation appears to be above the target, the bank is likely to raise interest rates. This usually has the effect over time of cooling the economy and bringing down inflation;
- if inflation appears to be below the target, the bank is likely to lower interest rates. This usually has the effect over time of accelerating the economy and raising inflation.
Under the policy, investors know what the central bank considers the target inflation rate to be and therefore may more easily factor in likely interest rate changes in their investment choices. This is viewed by inflation targeters as leading to increased economic stability.
The United States Federal Reserve, the country’s central bank, practices a version of inflation targeting. Instead of setting a specific number, the Fed sets a target range.
Importance Of Money
Criticisms of Inflation Targeting
Increases in inflation, measured by changes in the consumer price index (CPI), are not necessarily coupled to any factor internal to country’s economy. Strictly or blindly adjusting interest rates will potentially be ineffectual and restrict economic growth when it was not necessary to do so.
Demand And Supply Of Money
It has been argued that focusing on inflation may inhibit stable employment and exchange rates. Supporters of a nominal income target also criticize the tendency of inflation targeting to ignore output shocks by focusing solely on the price level. They argue that a nominal income target is a better goal.